News
Soil Fatigue: Discover Causes and Expert’s Remedies
News _ 30 NOVEMBER _2017
It happens in agricultural fields as well in gardens: gradually, year after year, the production decreases, even though the cultivation technique remains the same. This is the typical effect called by the agronomists “soil fatigue”, that is a field fertility loss done by unidentified causes. Let’s see which are the causes of this phenomenon and how to solve it.
Soil fatigue is a pretty common phenomenon, but is not always spotted, mainly because the production decrease is not so huge to worry the farmer.
Its causes may be different, but basically the main ones can be considered three: reduction of nutrients; presence of root exudates in the soil; extraordinary presence of parasites and pathogens which cannot be seen by eye.
In contemporary agriculture, where is present a high level of fertilizers, it is difficult to ascribe the soil fatigue to the lack of some macro-element. It’s more common, but rare anyway, that can be detected an insufficient availability of one or more micro-elements. In this case, the plant manifests symptoms which permit to recognize the nutritive scarcity and to find out a remedy. Because is simple to intervene with the fertilizers (micro and 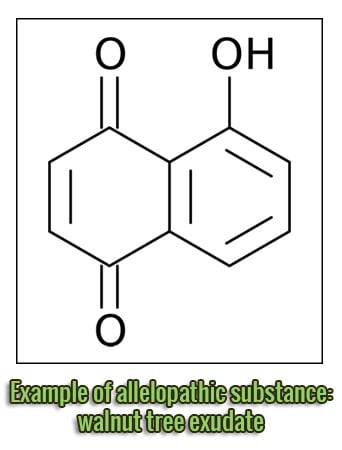
The plants’ roots construct a deep and complex relationship with the soil. For example, they release substance to aid helpful microorganisms’ development; they also produce substances which can impede the development of roots of similar or equal plants types/families. These substances, called allelopathic, have, sometimes, a slow degradation, and may also persist in the soil for a long period of time. Some cultivated species are more efficient: between the horticultural crops, pepper, potato, and more in general all the Solanaceae; between the fruit-production, apple tree, walnut tree and more in general stone fruits; among the weeds, the Cyperus, sorghum and wheatgrass; amidst extensive and legumes crops even though in a lower measure compared to the other species.
The third cause can be reconducted to the massive presence of one or more crops pathogens and parasites. The phenomenon may be imputed to a gradation (fast increase) of these organisms, due to a reiteration of the same crop on the same field, without respecting the proper year range before restarting the cultivation. This is a true fact, especially for crops like tomato, potato, sugar beet, tobacco etc.; in other words, for those crops which include a large number of specific and non-specific parasites.
The soil
Often though, the soil fatigue strongly manifests only in presence of impaired soil agronomical conditions. Let’s see why.
The chemical-physical degeneration of the soil is caused by a loss of porosity and by a huge reduction of organic matter. Especially on loamy and clayey soil, the trampling effects are detrimental because mechanically reduce the soil porosity. Less gas exchanges between the soil and the atmosphere, frequent water stagnation, even worse the drought phenomes, all of these instances lead to soil acidification and the alteration of normal biological cycles. The farmer usually deals with these problems by a more intense field preparation, generating a negative cause-effect spiral in the long period.
In fact, when the plow is used as main instrument for soil preparation, excessive soil oxygenation happens, causing on one hand soil asphyxia phenoms reduction (positive), but on the other hand leads to humus oxidation and living biomass reduction in the soil (negative). The reduction of organic matter presence, provokes an acceleration of the soil impoverishment.
Few organic matter, reduced microbiological activity, total loss of natural soil structure and frequent intensive procedures for soil porosity restoration, represent the ideal conditions for pathogens and parasites species gradation.
To this as to be added the reduction of soil capacity of keeping and exchanging the nutrients with the water which circulates in the soil (circulating solution) and, when the soil pH variation happens, also the chemical alteration of the soil, causing problems as well for nutrients availability.
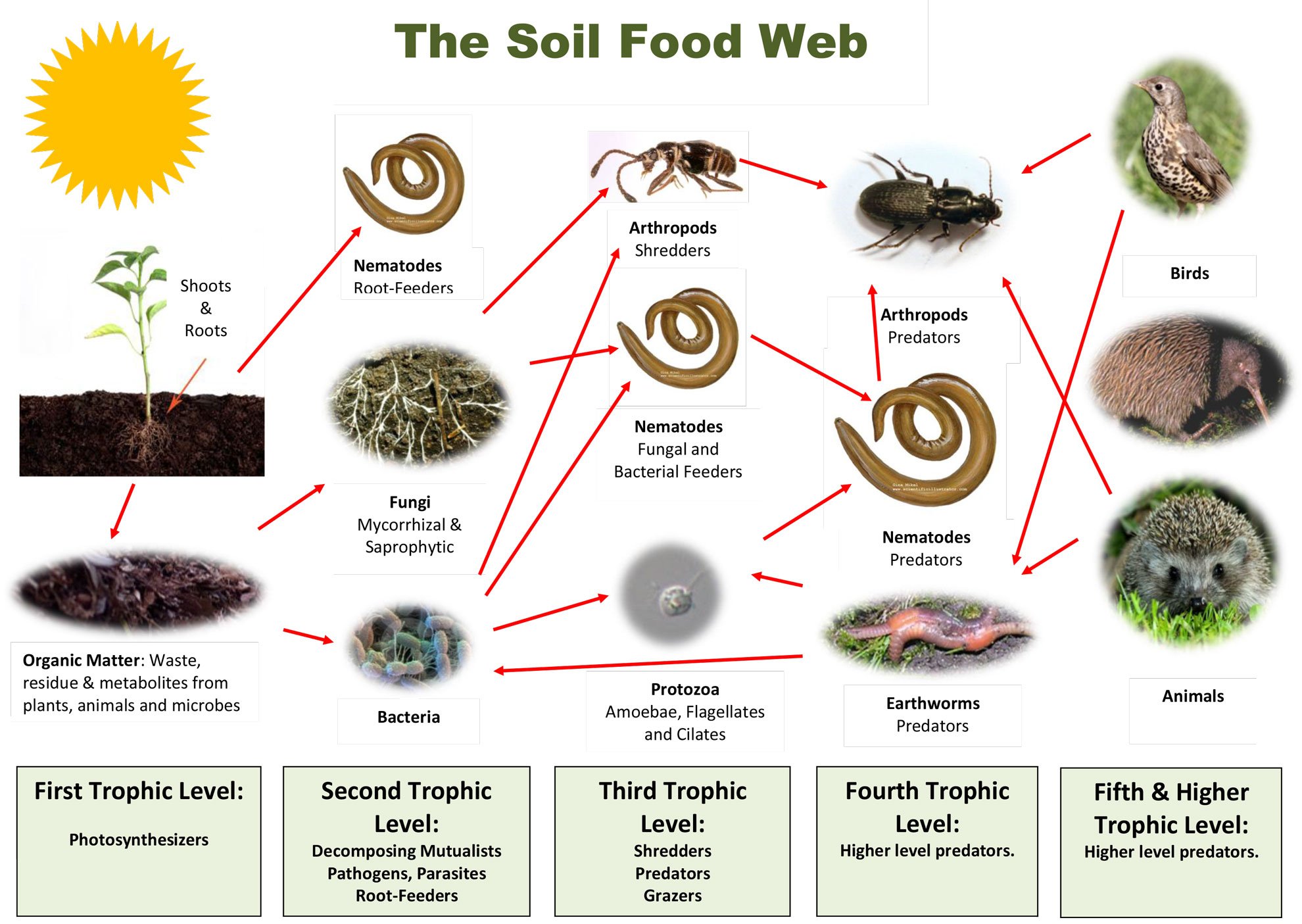
The terrain well handled, within the first 20-40cm is full of life: other than a macro-fauna represented especially by earthworms (Darwin considered the earthworm as the most helpful organism to mankind and ecosystem to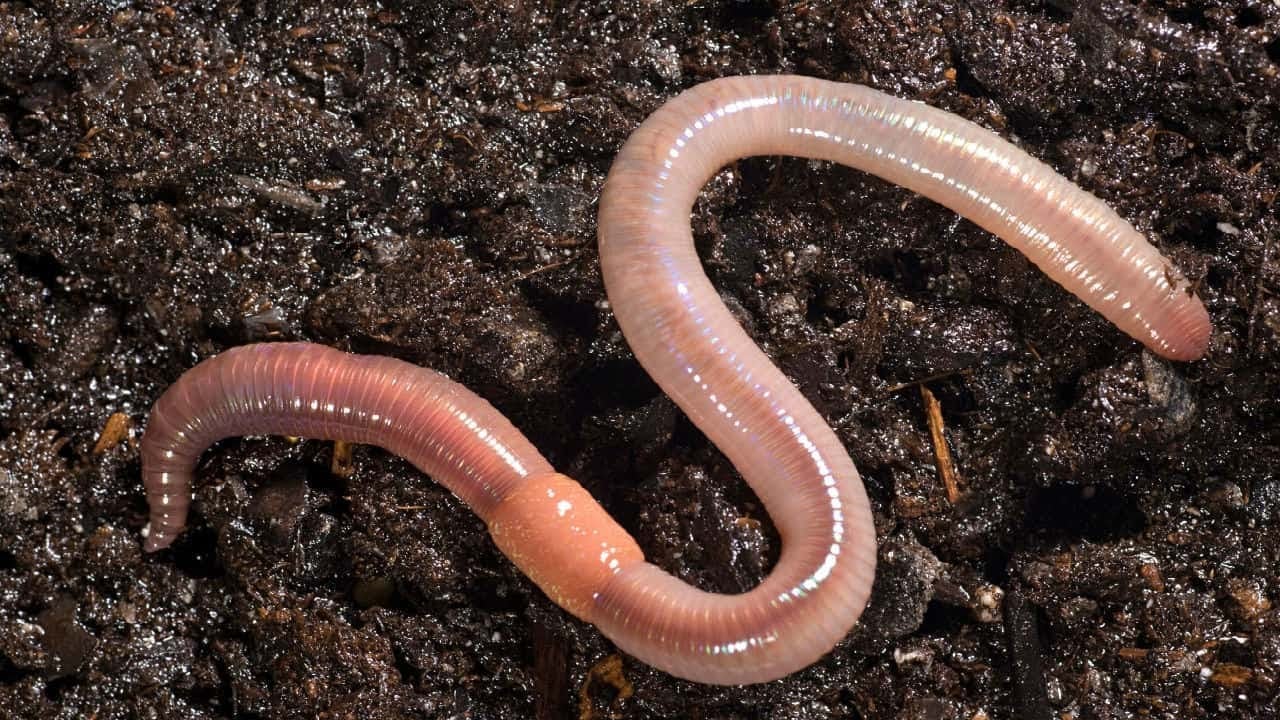 
A soil which is microbiologically active, is also capable of decompose more quickly the allelopathic substances emitted by the plants and turn them ineffective.
In the agricultural field, keeping a high level of biodiversity and augmenting the content of organic matter is possible only by using particular management techniques whose reduce the soil disturb, augment the availability of vegetable material on the field, guarantee soil cover, help to maintain a balanced soil porosity, limit chemical-mineral fertilization only where is strictly necessary, according to crop needs.
A difficult path which imposes a critical revision of the cultural processes management and which can be facilitated by the introduction of techniques derived from precision agriculture and conservative agriculture.
Soil fatigue: preventing is better than healing
In order to prevent the soil fatigue is necessary to understand the indications provided by the modern agronomy which can be reassumed in this way:
- Crop rotation with different botanic families’ integration;
- To distance in proper manner those crops which are more vulnerable to pest bruises;
- To insert cereals between straw and/or corn in the crop rotation process (crops which produce a large quantity of residues);
- To abandon the use of stubble burning technique (forbidden) leaving on the field the cultural residues produced by cereals instead;
- To seed other manure crops or cover-crops;
- To fertilize in a balanced way and, when possible, have recourse to organic fertilizing;
- To avoid the soil compaction by equipping agricultural vehicles with proper moving organs (treads, low pressure tires and twin wheels);
- To adopt soil preparation techniques which can reduce soil disturb, by choosing implements with disks and tines instead of the mouldboard, that is replacing the plow in favour of implements with straight tines and proper implements for soil decompaction.
In the horticultural world is not easy to respect all these indications without the disposal of various fields.
How to remedy
In case of soil fatigue phenomenon, it’s important to spot the causes at its origin. The expert, as the doctor, will start to investigate about the previous techniques adopted (history), will examine plants roots and their collar to find out possible pathogens (nematodes? Fungus?…) and finally, will check the upper part of the plant (outside the soil) to verify potential specific symptoms. Thereafter will issue a therapy, but in these cases the remedies are always “painful”.

Cover-crops as well as manure crops are very helpful but they have to be selected with accuracy. In fact, in case of biological cause (nematodes, fungus, bacteria…) crop species should not be able to host parasites. It would be even better if the plants could combat these parasites, just like Brassicaceae manure crops which act in a rather positive way against parasites.
More in general, for some soil fatigue causes it’s possible to adopt inexpensive biological war strategies, for other cause is not possible.
If the crop cannot be suspended, the use of chemical treatments for the soil is unavoidable; usually are used liquid products or solid ones with fumigant action. The use of this products, which release isothiocyanates in the soil, are subjected to mandatory provisions by the European Community.
In this case, the use of implements able to distribute these products according to proper doses and methods, is essential because of the high costs of the treatment, also for preventing environment damages and respecting European rules.

We still have to focus on the prevention by the way. Both the cures, biological or chemical, don’t produce long lasting effects, but they have to be accompanied by a revision of production process management. A smart crops rotation is still the most effective method to avoid and remedy to this phenomenon.
Conclusion
In this article we explained what is the soil fatigue phenomenon, which are its causes, how to prevent its appearance and, in the end, how to remedy. As anticipated, is not always clear when this problem appears, because the production variations may be at minimum level.
We suggest to execute all the possible precautions to prevent it and make periodical controls of the soil estate, in order to spot its eventual presence and find a remedy.
In case of more doubts or need of further information about the remedies to this phenomenon, don’t hesitate to contact us. Our team of experts Forigo will be glad to supply you with all the information you requested.

Research and Development Division of Forigo Roteritalia. Team of experts engaged in the study and analysis of the main agricultural and horticultural techniques used today. Knowledge combined with competence are the starting point for continuous improvement in a scenario of innovation and technological development.
Upcoming Exhibitions
Previous Exhibitions
30 MARCH 2025
Forigo at Agriumbria 2025: quality in soil preparation
07 FEBRUARY 2025
Forigo at Fruit Logistica 2025: towards more efficient agriculture